MultiMechanics and Opterus R&D Set up Partnership to Create Advanced Material Models in Response to NASA Solicitation

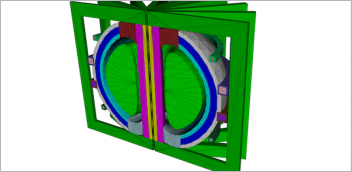
The MultiMechanics – Opterus collaboration will develop accurate, validated and usable software to predict the behavior of HSC structures, according to MultiMechanics. Image courtesy of MultiMechanics
Latest News
October 16, 2018
MultiMechanics, a developer of multiscale composite modeling and simulation software, and Opterus R&D, a Colorado-based satellite component manufacturer specializing in the design and testing of deployable space structures, have announced a collaboration in response to a NASA Solicitation seeking further exploration of the use of thin-ply high strain composites (HSCs) for space applications. These advanced composites have the potential to reduce weight and increase the performance of space systems, but they exhibit behavior that is difficult to predict using currently available finite element analysis (FEA) tools.
Thin-ply HSCs are being used by Opterus in several commercial, NASA and DoD missions that achieve packaging and deployed stiffness performance. Compared to traditional composites, HSCs exhibit improved damage tolerance, resistance to microcracking, improved aging and fatigue resistance, reduced minimum-gauge thickness and increased scalability.
However, HSC materials behave in a complex manner that is difficult to predict. Strain levels in HSCs are up to 3x higher than in traditional composites, causing behaviors that are nonlinear with fiber tensile stiffening and compression softening and sensitive to creep and stress relaxation. Expensive, iterative physical testing is currently being used to study the loading-deformation and failure response of HSCs. The MultiMechanics – Opterus collaboration will develop accurate, validated and usable software to predict the behavior of HSC structures, according to MultiMechanics.
In response to a NASA Solicitation and in order to accelerate the adoption of HSCs for space applications, Opterus R&D will create material models of HSCs that can be used in currently-available FEA systems. MultiMech will be used in this development due to its unique capabilities to model rate-dependent material behavior, a critical feature presented by HSCs.
“MultiMechanics offers the most computationally efficient material modeling platform, along with the broadest range of material options,” stated Dr. Thomas Murphey, President at Opterus R&D. “In addition to the advanced capabilities of their software, the MultiMechanics team has also shown an interest in and willingness to support the growing HSC community.”
Phase I of the program is to generate test data, exercise the current commercial version of MultiMech, and identify the best path forward to confirm that MultiMech can address all HSC analysis needs in the future. In Phase II, MultiMechanics will take a larger role aimed at implementing features specific to solving HSC engineering challenges.
“HSCs exhibit high potential for reduced weight and increased performance for several space applications,” says Dr. Flavio Souza, president and CTO at MultiMechanics. “We are proud to support Opterus R&D and the entire HSC community in their mission to accelerate the adoption of these promising materials.”
For More Info
Subscribe to our FREE magazine, FREE email newsletters or both!
Latest News
About the Author
DE’s editors contribute news and new product announcements to Digital Engineering.
Press releases may be sent to them via [email protected].