November 30, 2015
Design is the key differentiator among products in today's economy, but predictability and iterative speed are key differentiators in the economics of design. At its heart, design engineering is the process of iteration: An idea is visualized, critiqued and refined, until it is ultimately delivered. More iterations mean more chances to try new ideas, to catch mistakes, to polish concepts into ever better designs. It’s not enough, however, to have a beautiful design. Speed to market and cost of production are both essential in the creation of a competitive, profitable product. While it’s important to do enough design iterations, the changes need to happen quickly and with the confidence that the final product will emerge as the designer intended.
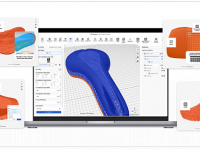
Rendering has long been an important tool for visualizing 3D designs. Real-time display renderers, such as OpenGL, lend themselves well to rapid iteration. However, such rendering can only approximate the appearance of materials and objects. It is often useful for working with the mechanical components of a shape, but it cannot accurately predict the appearance of a finished product, meaning the designer can only make educated guesses.
Various forms of ray tracing and other CPU-based rendering methods that simulate light more realistically than OpenGL have been available to designers for years, but these have been difficult to use and too slow to fit well into rapid iterative design. As a result, many designers have simply learned to do without realistic rendering, or they have saved it for special occasions.
Interactive, predictive, physically based rendering (PBR) is poised to change the way such designers work. It combines easy-to-use physically based lighting, verifiable realistic materials and reliably accurate photorealistic results, with the computational performance of graphics processing units (GPUs). Not only can a designer see how the product will really look, he can see it in his application’s interactive viewport, while he designs it. Just as hardwareaccelerated OpenGL became the standard mode for working interactively in 3D, GPU acceleration turns physically based rendering into an interactive design mode that will become an essential part of iterative design workflows.
Fill out the information below to download the resource.
Latest News